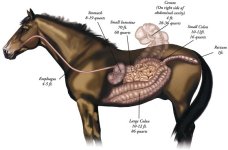
Veterinarian Anthony Blikslager discusses the likely direction of future research into colic and argues the need for more investment in studying the problem.
Colic continues to be a serious health concern for horse owners and the equine industry.
Studies indicate that about 10% of the horse population will suffer an episode of colic each year and that about 0.7% will die from colic.
Based on the American Horse Council's estimated population of 9.2 million horses in the United States, about 920,000 cases of colic occur each year, and more than 64,000 horses may die due to colic-related problems.
Colic not only causes horse owners heartache, but it creates a major economic loss to the horse industry.
Given the American Horse Council's estimation that the horse industry generates $US102 billion toward the US gross domestic product each year, the annual monetary loss from colic would exceed $700 million.
Colic cases are categorized as either surgical or medical. The leading cause of colic-associated deaths is intestinal strangulation, which causes death of the intestine and absorption of toxins that lead to fatal shock.
Fortunately, the great majority of horses that suffer from colic do not require surgery, with most being treated successfully with medical care. Although medically treated cases of colic have a very low mortality rate, they represent the greatest burden of this disease syndrome. Colic of any origin is of great concern to owners and results not only in suffering for the horse, but also in costs associated with loss of use and veterinary care.
To decrease the incidence of colic and save the lives of horses requiring surgery, horses and groups of horses will need to be critically examined and research completed to find the reason for the various intestinal disorders that cause colic.
This will require new knowledge about nutrition, pasture management and stabling.
In recent years, researchers have determined that high concentrate diets, changes in diet, increased stabling time and other management practices can increase the risk of colic. These factors do not, however, explain all cases of colic.
Further research is needed to elucidate management practices and other characteristics that increase the risk for colic. Once identified, clinical studies are needed to determine the effects of altering specific management practices. This will require large-scale studies, possibly involving horses from several countries, to identify management techniques and other factors associated with colic.
The costs of this type of research principally involve personnel required to collect, enter and analyze data, rather than the purchase of supplies and equipment. Following horses during such studies requires a dedicated, competent team and significant financial backing to complete the needed research.
Increasing survival in horses that have life threatening types of colic involves four approaches:
* Early referral;
* Curtailing intestinal injury;
* Hastening intestinal repair;
* Reducing the development of complications.
Early referral continues to be one of the most important ways to decrease the mortality associated with serious diseases. Investigations are needed to identify clinical or laboratory signs indicative of disease severity that can be used to improve the veterinarian's ability to make an early referral for horses requiring intensive care and possibly surgery.
Preventing further injury of the obstructed or strangulated intestine requires a better understanding of ways to resuscitate the affected tissue when its blood supply has been restored.
Similar to the damage that occurs to the heart muscle in humans after blood flow has been restored after a heart attack, restoration of intestinal blood flow, known as reperfusion, also causes intestinal injury beyond what occurred during the strangulation.
Studies are needed to determine whether the mechanisms responsible for reperfusion injury in laboratory and small animal species are the same in horses, and to identify new treatments to reduce the degree of damage occurring in the strangulated intestine.
This approach will require considerable resources to study the basic mechanisms of cell death and survival in the equine intestine, followed by clinical trials to test novel treatments capable of interfering with these mechanisms.
Research to identify treatments that can optimize intestinal healing while decreasing inflammation is needed to help improve survival in horses after surgery.
While anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used to ameliorate signs of endotoxin-induced shock and the pain of colic, they also block production of prostaglandins, which are important for normal physiology and healing.
As a result, many of the NSAIDs can impair intestinal healing after surgery. Research is needed to identify NSAIDs or other drugs that can control pain and shock while maintaining the normal physiologic processes in horses with colic.
Studies also are needed to improve our ability to prevent the development of complications that occur all too often in horses with gastrointestinal diseases causing colic.
Some of these complications include post-operative ileus (absence of normal intestinal movement), the development of intestinal adhesions, intravascular clots and laminitis. Only by addressing gaps in our knowledge about the development of these complications can improvements be made in the quality of a horse's life after colic.
Teams of equine researchers with expertise in epidemiology, clinical trials and basic science are needed to make progress in each of these areas.
Within the US and United Kingdom alone, these individuals are available and many currently work together in collaborative studies.
The critical component missing is adequate funding for colic research.
Considering the huge cost of colic to horse owners and the equine industry, the cost to complete research studies is relatively small. Therefore, now is the time to invest in research on a problem that is of critical importance to the horse.
by Anthony Blikslager, DVM, PhD, Dipl. ACVS on behalf of the Equine Research Coordination Group
The Morris Animal Foundation (
www.morrisanimalfoundation.org), American Quarter Horse Foundation (
www.aqha.com/foundation), Grayson Jockey-Club Research Foundation (
www.grayson-jockeyclub.org) and the American Association of Equine Practitioners Foundation, Inc. all support work in this area. Alternatively, contact your favorite veterinary school to support colic research. Please contact the AAEP Foundation (
www.aaepfoundation.org) for information about how to make donations for equine research, or call 1-800-443-0177 (within the U.S.) or 859-233-0147. This is just one of many efforts that the AAEP is coordinating on behalf of the industry through the Equine Research Coordination Group (ERCG), which is comprised of researchers and organizations that support equine research. ERCG was formally organized last year with a mission of advancing the health and welfare of horses by promoting the discovery and sharing of new knowledge, enhancing awareness of the need for targeted research, educating the public, expanding fundraising opportunities and facilitating cooperation among funding agencies.
The mission of the Equine Research Coordination Group (ERCG) is to advance the health and welfare of horses by promoting the discovery and sharing of new knowledge, enhancing awareness of the need for targeted research, educating the public, expanding fundraising opportunities, and facilitating cooperation among funding agencies.
The ERCG is a group comprised of researchers and organizations that support equine research. Participants in the ERCG include equine foundations and multiple university research representatives. Current participants include: AAEP Foundation, American Horse Council, AQHA Foundation, Grayson-Jockey Club Research Foundation, Maxwell H. Gluck Equine Research Center, Morris Animal Foundation, Havemeyer Foundation, United States Equestrian Federation Foundation and University Researchers including: Noah Cohen, VMD, PhD (Texas A & M University), Greg Ferraro, DVM (University of California � Davis), Eleanor Green, DVM (University of Florida), Dick Mansmann, VMD, PhD (North Carolina State University), Wayne McIlwraith, BVSc, PhD (Colorado State University), Jim Moore, DVM (University of Georgia), Rustin Moore, DVM, PhD (The Ohio State University) and Dr. Nat White DVM (Virginia Tech). For more information about the ERCG, please visit online at
http://www.aaepfoundation.org and click on the ERCG link.